Cisco - Configuring OSPF Router IDs and Why They Matter
Learn how to set and manage the OSPF router ID on Cisco devices, understand defaults, best practices, and how to force a fixed ID.
When preparing for your CCNA, CCNP, or CompTIA Network+ exams, there’s a good chance you’ll run into questions about OSPF (Open Shortest Path First). One key detail that often trips people up, both in exams and real-world deployments, is the Router ID (RID). Understanding how it works, how to configure it, and why it matters can be the difference between a stable OSPF environment and hours of troubleshooting.
Let’s break it down in a simple, exam-focused way.
🚦 Why Should You Care About OSPF Router IDs?
Imagine you’re managing a network of delivery trucks. Each truck needs a unique ID so you can track its location and path. If two trucks have the same ID, your tracking system gets confused, making your deliveries a mess.
In OSPF, routers are those trucks; the Router ID is their license plate. It’s how OSPF identifies and distinguishes each router in the OSPF domain.
Why It Matters:
- Stability: Router IDs are used to form adjacencies and elect DR/BDR (Designated Router/Backup Designated Router).
- Troubleshooting: The Router ID appears in logs and command outputs when looking at OSPF routes or adjacency issues.
- Deterministic Behavior: Properly configuring Router IDs ensures that router behavior is predictable and repeatable, especially after reboots.
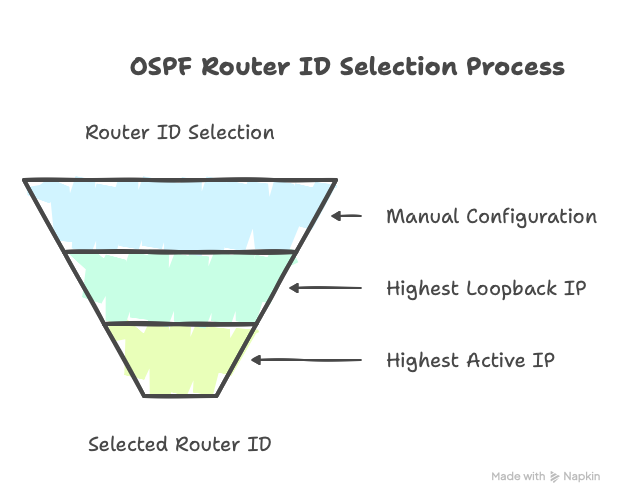
🔍 How OSPF Chooses the Router ID (Default Behavior)
OSPF picks one automatically if you don’t manually configure a Router ID. Here’s the order:
- Manually configured Router ID (using the
router-idcommand) - Highest IP address on a loopback interface
- Highest IP address on any active physical interface
📘 Real-World Analogy:
Think of this like choosing a username online:
- If you pick a unique one yourself (
router-id), that’s what’s used. - The system picks your most unique email (loopback IP) if you don't.
- It grabs your most-used address (physical IP) if you don't have that.
🛠️ How to Configure a Router ID in OSPF (Step-by-Step)
Let’s walk through configuring an OSPF Router ID on a Cisco router.
Step 1: Enter OSPF Router Configuration Mode
R1(config)# router ospf 1
Step 2: Set the Router ID
R1(config-router)# router-id 1.1.1.1
🔁 Note: This command does not take effect until you reset the OSPF process or reboot the router:
R1(config-router)# clear ip ospf process
🧪 Lab Example: See Router ID in Action
You have two routers: R1 and R2. You want to manually configure Router IDs so they don’t change on reboot.
On R1
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
On R2
router ospf 1
router-id 2.2.2.2
Use the command below to verify Router ID:
R1# show ip ospf
Output:
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 1.1.1.1
You’ll see this ID in:
show ip ospf neighborshow ip ospf database- OSPF LSAs
- Wireshark packet captures
⚠️ Common Pitfalls (And How to Avoid Them)
❌ Forgetting to Clear the OSPF Process
- If you configure the Router ID after OSPF is already running, it won’t take effect until a restart.
- Use:
clear ip ospf process(but only during a maintenance window in production!)
❌ Loopback IP Not Set
- OSPF prefers loopbacks for Router ID selection, but if you forget to configure them, it falls back to physical IPs, which may change.
❌ Duplicate Router IDs
- Having the same Router ID on two routers breaks OSPF adjacencies. Always verify uniqueness.
🎯 Exam Insights
If you’re prepping for CCNA or CCNP:
- Expect questions on how Router ID is chosen.
- Know the order of selection and what command is used to configure it.
- Be ready to identify Router ID issues in simulated troubleshooting scenarios.
For CompTIA Network+:
- Focus more on how OSPF works and why unique IDs are important.
- You may not need to configure it directly, but know how it impacts route discovery and network stability.
✅ Summary: Key Takeaways
- OSPF Router ID is a unique 32-bit identifier (looks like an IP, but it’s not routable).
- You can set it manually using
router-id X.X.X.Xthe OSPF config mode. - If not set manually, OSPF uses:
- Highest loopback IP
- The highest physical interface IP
- Always reset the OSPF process to apply Router ID changes.
- Make Router IDs consistent and predictable, especially in large networks.